Generative AI vs. LLM: A Comparative Analysis
Key Insights
- Generative AI and LLMs are two powerful technologies revolutionizing various industries
- Generative AI focuses on creating new and unique data, while LLMs specialize in language understanding and generation
- Both technologies have their strengths and weaknesses, making it important to understand their differences
- By comparing their functionality, flexibility, efficiency, and accuracy, businesses can make informed decisions on which technology to adopt
Understanding the Basics of Generative AI
Generative AI refers to an advanced form of artificial intelligence that has gained traction in recent years. It involves the creation of new and original data based on patterns and examples from existing information. This technology is capable of generating images, text, music, and even videos that closely resemble human-created content.
Defining Generative AI
Generative AI encompasses a range of algorithms and techniques that enable machines to produce creative and innovative outputs. Through machine learning models like generative adversarial networks (GANs) and variational autoencoders (VAEs), generative AI systems can learn from vast amounts of data and generate new samples with realistic features.
Key Features of Generative AI
Generative AI possesses several notable features that set it apart from other AI technologies. Generative AI models, like other AI systems, learn from extensive datasets to identify patterns, styles, and structures. However, what sets generative AI apart is its ability to use this data to create new content and produce highly imaginative outputs that were not explicitly provided during the training process.
- Example: Generative AI can be used to create mesmerizing landscapes that blend elements from different geographical locations, resulting in breathtaking scenes that have never been seen before.
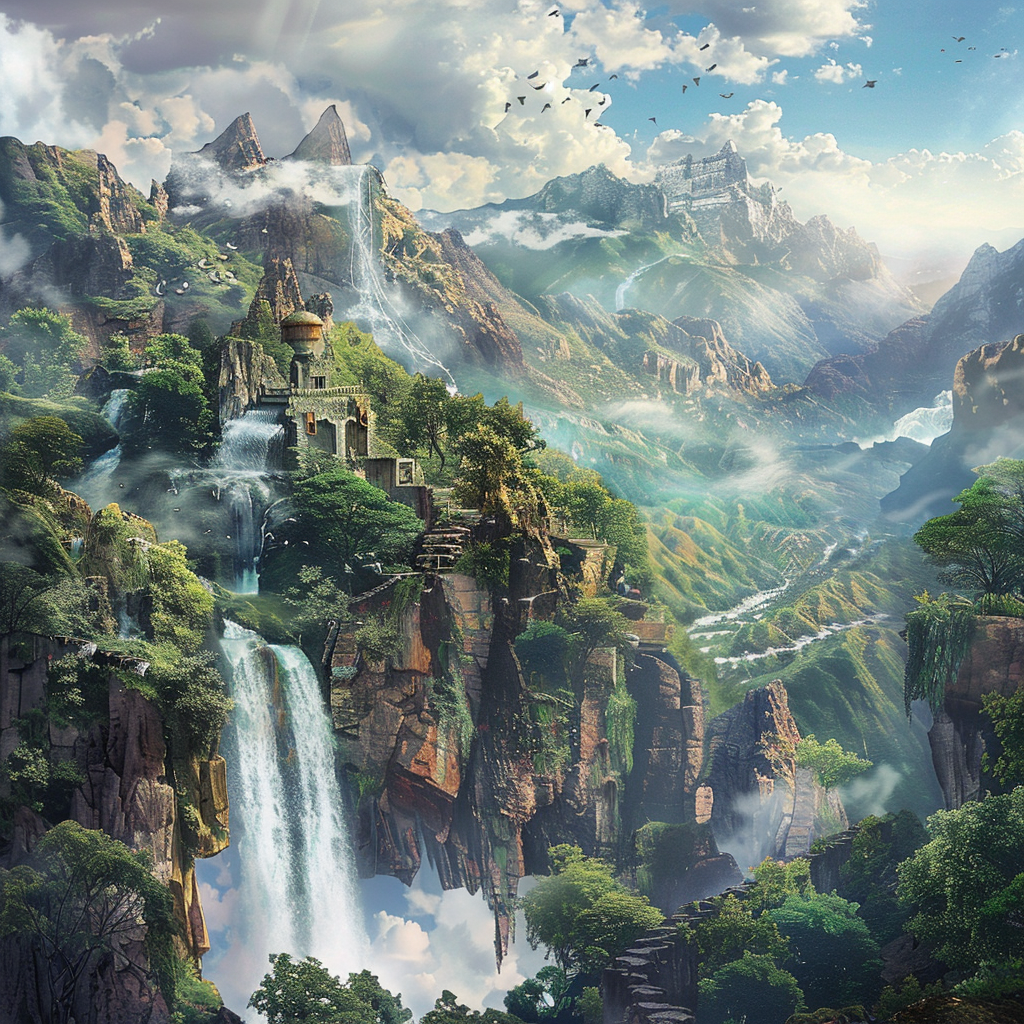

Imaginary geographical location generated with Midjourney.
To enhance the outputs of generative AI, users can engage in an interactive and iterative feedback process. This continuous feedback loop enables the AI to learn and adapt to user preferences, becoming more attuned to the subtle nuances of the creator’s intent and better results over time.
These models are also capable of adjusting to different inputs and conditions, generating outputs tailored to user-defined parameters like color schemes, art styles, or musical styles.
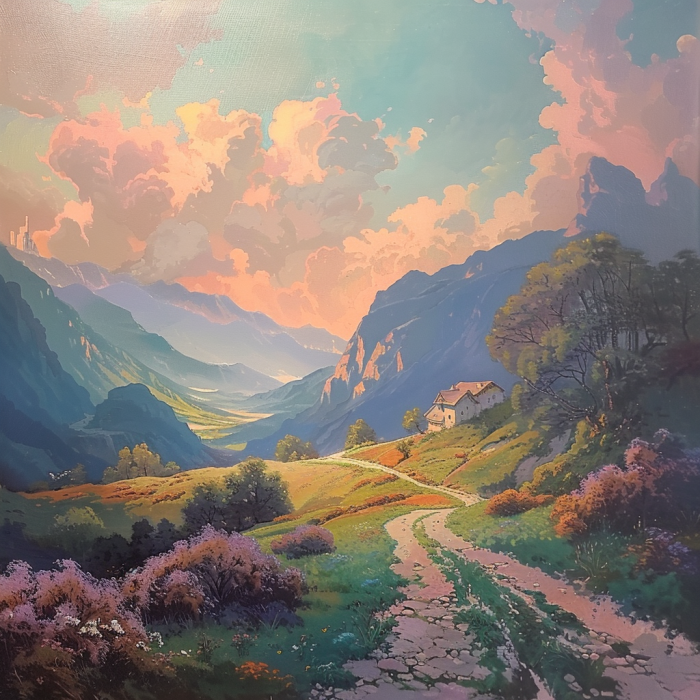
- Example: When provided with parameters like a pastel color palette and landscape theme, generative AI can depict a unique landscape using soft colors.

Pastel landscape generated with Midjourney.
Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI is transforming content creation and service delivery across various industries with its advanced capabilities.
Art & Content Creation
Generative AI serves as a powerful tool for both everyday creators and professional artists. For individuals, it democratizes content creation by providing easy-to-use platforms that generate high-quality written, visual, and audio content. This technology enables people to create blogs, artwork, or music without needing extensive technical skills, fostering creativity and personal expression across diverse communities.
For artists, generative AI acts as a collaborative partner, offering new avenues for creativity and innovation. This collaboration allows artists to push the boundaries of their traditional mediums and explore new artistic territories, enhancing their work with unique elements that can be tailored to specific artistic visions and styles.
In marketing, generative AI is instrumental in creating personalized content that resonates with diverse audiences. It is used to generate customized emails, social media updates, and scripts for digital content. This boosts customer engagement and optimizes marketing strategies by integrating consumer data and feedback into content creation.
Media & Entertainment
In the film industry, AI aids in creating complex storylines and sophisticated visual effects, enabling filmmakers to produce high-quality content more quickly and economically. In the music sector, generative AI assists in composing melodies, writing lyrics, and inventing new sound effects, which allows artists to explore and create unique musical styles and harmonies.
Additionally, journalists and authors benefit from generative AI by automating aspects of research and writing. For journalists, AI tools quickly gather and synthesize information, aiding in the creation of timely and factually accurate articles. Authors use generative AI to explore different narrative possibilities and develop rich, engaging content, often enhancing the creative process by suggesting plot developments and character traits to enrich the storytelling experience.
AI Model Development
Generative AI is crucial for creating synthetic data, which is used to train AI models. This synthetic data closely mimics real-world variations, enhancing the training process by providing rich, diverse datasets. This improves the accuracy and applicability of AI models across various fields, enabling them to perform reliably in diverse scenarios.
Delving Into the World of LLMs
LLMs, also known as large language models, are deep learning models that have been designed to understand and generate human-like written language. These models have achieved remarkable success in natural language processing tasks, such as language translation, text summarization, and question-answering.
Unique Characteristics of LLMs
Built on a neural network architecture known as the Transformer, large language models are trained by processing and learning from an extensive corpus of text that include books, articles, websites, and other forms of written communication. This training helps them master the intricacies of language, such as grammar, context, and cultural idioms. A key feature of LLMs is their self-attention mechanism, which allows the model to evaluate the relevance of each word in a sentence, helping enhance the model’s understanding of context.
Once trained, LLMs can perform a wide array of language-based tasks, such as generating coherent and context-appropriate text, answering questions, summarizing long documents, translating between languages, and even creating creative content like poems or news articles. The versatility and utility of LLMs arise from their ability to comprehend and manipulate language with a proficiency that approaches human-like levels.
Fine-tuning a large language model for a specific domain significantly improves its ability to interpret and generate text suited to specialized needs. This process involves training the model further with a dataset tailored for a particular sector, like finance, law, or healthcare. By doing so, the model becomes adept at understanding the unique jargon and stylistic nuances of that field. This targeted approach makes fine-tuned models invaluable for industries looking to leverage AI for more precise and efficient communication and data analysis.
Uses of LLM in Various Industries
The integration of large language models across various industries showcases the extensive capabilities of AI to revolutionize traditional processes. Here’s a closer look at the applications of LLMs in different sectors.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, LLMs play a pivotal role by automating medical documentation. This improves the accuracy of patient records and enhances the efficiency of administrative tasks. By reducing the manual burden on healthcare providers, LLMs allow them to focus more on patient care rather than paperwork.
Customer Service
Customer service has seen significant improvements with the introduction of LLMs. These AI tools manage customer inquiries and support transactions through automated systems like chatbots and virtual assistants. This automation increases operational efficiency and improves the customer experience by providing quick and reliable responses to queries.
Law
The legal sector benefits from LLMs through enhanced document analysis and generation. Legal professionals use these models to draft, review, and summarize complex legal documents, significantly increasing their workflow efficiency. Additionally, LLMs aid in legal research by quickly locating relevant case laws, statutes, and precedents.
Education
In education, LLMs are tailored to fit the individual learning styles and paces of students. They provide real-time feedback, answer queries, and assist educators in creating and grading tests. This reduces the educators’ workload and allows them to dedicate more time to direct student interaction, enhancing the learning experience.
The Core Differences Between Generative AI & LLMs
While both generative AI and LLM fall under the umbrella of artificial intelligence, their focus and capabilities differ significantly.
Functionality & Performance
Generative AI excels in creating new and unique data, while LLMs showcase remarkable language understanding and generation abilities. Generative AI allows for the generation of various multimedia outputs, while LLMs primarily focus on textual language tasks.
Flexibility & Adaptability
Generative AI systems can adapt and generate diverse outputs based on user input and feedback. In contrast, LLMs exhibit greater flexibility in understanding context and adapting to different textual domains.
Efficiency & Accuracy
Efficiency-wise, generating new media content using generative AI can be time-consuming due to the intricacy of the generated outputs. Conversely, LLMs demonstrate faster response times as they primarily deal with textual processing. In terms of accuracy, generative AI outputs may have some variations and occasional inconsistencies, while LLMs have been optimized for generating coherent and precise written language.
Strengths & Weaknesses of Generative AI & LLM
By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of both generative AI and LLM, businesses can make informed decisions on integrating these technologies into their operations.
Pros & Cons of Generative AI
Generative AI offers unparalleled creativity and innovation, allowing businesses to explore new possibilities. It enables content generation at scale and has broad applications in various creative industries. However, the generated outputs may lack consistency, and controlling the output quality can pose challenges. The enormous computational power required to train and generate data can be a limiting factor for smaller organizations.
Advantages & Disadvantages of LLMs
LLMs provide accurate and contextually appropriate language generation, creating opportunities for enhanced customer interactions and improved content creation. Their ability to grasp complex linguistic nuances drives their success in language-related tasks. However, LLMs heavily rely on the vast amounts of training data, and without proper data curation, biases and misinformation may be propagated. Additionally, fine-tuning LLMs to specific domains can be a resource-intensive process.
The decision to choose between generative AI and LLM depends on the specific requirements and objectives of each business. By understanding their functionalities, strengths, and weaknesses, organizations can harness the benefits of these technologies and improve their operations in various domains. Ultimately, a thoughtful assessment of the desired outcomes will guide businesses in selecting the technology that best aligns with their goals and objectives.
Empower Your Business With WestLink’s Cutting-Edge AI Solutions
As you navigate the complex landscape of Generative AI and LLM, WestLink is your ideal partner for implementing these transformative technologies. With over 7 years of experience and a track record of 100+ happy clients, our expert team specializes in custom cloud native software solutions that leverage the latest in machine learning, artificial intelligence, and more. Ready to transform your company with WestLink’s innovative and data-rich solutions? Learn more about how we can help you achieve your goals!
Questions?
- What is the fundamental difference between Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs)?Toggle questionWhile both Generative AI and LLMs involve generating content, the key distinction lies in their primary focus. Generative AI encompasses a broader category of models capable of creating diverse content beyond language, including images and music. On the other hand, LLMs, as the name suggests, are specifically tailored for generating and understanding language-based content.
- How do Generative AI and LLMs differ in their training approaches?Toggle questionGenerative AI models are trained on a more varied dataset that includes multiple types of content, fostering creativity across different domains. LLMs, however, are usually trained on vast amounts of text data, emphasizing language-centric understanding and generation.
- Can Generative AI models be used for tasks other than language-related applications?Toggle questionAbsolutely! Generative AI is versatile and can extend its capabilities to various domains such as art, music, and image generation. Its flexibility allows for a broader range of creative applications beyond language processing.
- What are the practical applications of Large Language Models (LLMs)?Toggle questionLLMs find applications in natural language understanding, text generation, chatbots, and language translation. They excel in tasks that involve processing and generating human-like text, making them valuable for a wide range of language-related applications.
- In terms of creativity, which model, Generative AI or LLM, offers more flexibility?Toggle questionGenerative AI, by virtue of its diverse training data, tends to offer more creativity and flexibility as it can generate content across multiple domains. LLMs, while proficient in language-related tasks, may have more constrained creativity in comparison.
- Can Generative AI and LLMs be used together in a single application?Toggle questionAbsolutely! Combining the strengths of both models can result in powerful applications. For example, using a Generative AI model for creative content generation and an LLM for refining and ensuring language coherence.

 hello@westlink.com
hello@westlink.com  (866) 954-6533
(866) 954-6533  700 N Colorado Blvd,
700 N Colorado Blvd,






Comments